Table per concrete class with Annotation
In previous article we saw Table per Concrete class using XML
In this article, we will learn the same using Annotation.
Let us understand about Table Per Concrete class with Annotation
Let’s create hibernate project using Annotation
Step 1
Create hibernate project
Please refer Hibernate setup in eclipse article on how to do it.
Project Structure
Step 2
Update pom.xml with Hibernate and Mysql dependencies
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <groupId>TablePerConcreteClassAnnotation</groupId>
- <artifactId>TablePerConcreteClassAnnotation</artifactId>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- <packaging>jar</packaging>
- <name>TablePerConcreteClassAnnotation</name>
- <url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
- <properties>
- <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>junit</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
- <version>3.8.1</version>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
- <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
- <version>5.2.6.Final</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>mysql</groupId>
- <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
- <version>6.0.5</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-annotations -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
- <artifactId>hibernate-annotations</artifactId>
- <version>3.5.6-Final</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- </project>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>TablePerConcreteClassAnnotation</groupId>
<artifactId>TablePerConcreteClassAnnotation</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>TablePerConcreteClassAnnotation</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-annotations -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-annotations</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6-Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Step 3
Create Employee class
- package com.kb.model;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
- import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
- import javax.persistence.Id;
- import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
- import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- @Entity
- @Table(name = "Employee2")
- @Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
- public class Employee {
- @Id
- @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
- @Column(name = "id")
- private int id;
- @Column(name = "name")
- private String name;
- @Column(name="city")
- private String city;
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getCity() {
- return city;
- }
- public void setCity(String city) {
- this.city = city;
- }
- }
package com.kb.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Employee2")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name="city")
private String city;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
@Entity annotation is used to indicate the class as persistent entity.
@Table annotation indicates the table name where this entity has to be persisted
@Inheritance annotation is used for implementing inheritance in hibernate.
It helps us to define the inheritance strategy.
We have used TABLE_PER_CLASS as inheritance strategy.
@Inheritance annotation is defined at root class level or sub hierarchy class level where different strategy has to be applied.
@Id is used to specify the primary key column.
@GeneratedValue is used to specify the primary key generation strategy.
@Column is used to specify the details of the column to which a field or property will be mapped
Step 4
Create PermanentEmployee class
- package com.kb.model;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- @Entity
- @Table(name = "PermanentEmployee")
- public class PermanentEmployee extends Employee {
- @Column(name = "salary")
- private double salary;
- public double getSalary() {
- return salary;
- }
- public void setSalary(double salary) {
- this.salary = salary;
- }
- }
package com.kb.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "PermanentEmployee")
public class PermanentEmployee extends Employee {
@Column(name = "salary")
private double salary;
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
Step 5
Create ContractEmployee class
- package com.kb.model;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- @Entity
- @Table(name = "ContractEmployee")
- public class ContractEmployee extends Employee {
- @Column(name = "hourlyRate")
- private double hourlyRate;
- public double getHourlyRate() {
- return hourlyRate;
- }
- public void setHourlyRate(double hourlyRate) {
- this.hourlyRate = hourlyRate;
- }
- }
package com.kb.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "ContractEmployee")
public class ContractEmployee extends Employee {
@Column(name = "hourlyRate")
private double hourlyRate;
public double getHourlyRate() {
return hourlyRate;
}
public void setHourlyRate(double hourlyRate) {
this.hourlyRate = hourlyRate;
}
}
Step 6
Create hibernate.cfg.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
- "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
- <hibernate-configuration>
- <session-factory>
- <!-- Database connection properties -->
- <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
- <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
- <property name="connection.username">root</property>
- <property name="connection.password">root</property>
- <!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
- <property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
- <!-- SQL dialect -->
- <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
- <!-- Disable the second-level cache -->
- <property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.internal.NoCacheProvider</property>
- <!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
- <property name="show_sql">true</property>
- <!-- Format the generated Sql -->
- <property name="format_sql">true</property>
- <!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update
- it -->
- <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
- <mapping class="com.kb.model.Employee" />
- <mapping class="com.kb.model.ContractEmployee" />
- <mapping class="com.kb.model.PermanentEmployee" />
- </session-factory>
- </hibernate-configuration>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection properties -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
<property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
<!-- SQL dialect -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Disable the second-level cache -->
<property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.internal.NoCacheProvider</property>
<!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- Format the generated Sql -->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update
it -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<mapping class="com.kb.model.Employee" />
<mapping class="com.kb.model.ContractEmployee" />
<mapping class="com.kb.model.PermanentEmployee" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
We have defined the entire database configuration in this file
hbm2ddl.auto property is defined in the config file which helps in automatic creation of tables in the database based on the mapping.
We have provided hbm2ddl.auto as Update so that it won’t delete any existing schema or tables, rather it will just update with new tables.
We have also provided the mapping class names where we have added the annotations using “mapping” tag.
Step 7
Create Hibernate util class
- package com.kb.util;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
- public class HibernateUtil {
- private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
- private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
- try {
- // Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
- return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- // Make sure you log the exception to track it
- System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
- throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
- }
- }
- public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
- return sessionFactory;
- }
- public static void shutdown() {
- // Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
- getSessionFactory().close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Make sure you log the exception to track it
System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
public static void shutdown() {
// Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
getSessionFactory().close();
}
}
Step 8
Create main class to interact with DB
- package com.kb.db;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import org.hibernate.Transaction;
- import com.kb.model.ContractEmployee;
- import com.kb.model.Employee;
- import com.kb.model.PermanentEmployee;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class Main {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- //Get session from Sesson factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- //Begin transaction
- Transaction t=session.beginTransaction();
- //Creating Employee base class record
- Employee employee=new Employee();
- employee.setName("John");
- employee.setCity("Newyork");
- //Creating Permanent Employee subclass record
- PermanentEmployee permanentEmployee=new PermanentEmployee();
- permanentEmployee.setName("Jacob");
- permanentEmployee.setCity("Delhi");
- permanentEmployee.setSalary(30000);
- //Creating Contract Employee subclass record
- ContractEmployee contractEmployee=new ContractEmployee();
- contractEmployee.setName("Raj");
- contractEmployee.setCity("Arizona");
- contractEmployee.setHourlyRate(2000);
- //persist all the employee records
- session.persist(employee);
- session.persist(permanentEmployee);
- session.persist(contractEmployee);
- //Commit the transaction and close the session
- t.commit();
- session.close();
- System.out.println("successfully persisted all the Employee records");
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.kb.model.ContractEmployee;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.model.PermanentEmployee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
//Get session from Sesson factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
//Begin transaction
Transaction t=session.beginTransaction();
//Creating Employee base class record
Employee employee=new Employee();
employee.setName("John");
employee.setCity("Newyork");
//Creating Permanent Employee subclass record
PermanentEmployee permanentEmployee=new PermanentEmployee();
permanentEmployee.setName("Jacob");
permanentEmployee.setCity("Delhi");
permanentEmployee.setSalary(30000);
//Creating Contract Employee subclass record
ContractEmployee contractEmployee=new ContractEmployee();
contractEmployee.setName("Raj");
contractEmployee.setCity("Arizona");
contractEmployee.setHourlyRate(2000);
//persist all the employee records
session.persist(employee);
session.persist(permanentEmployee);
session.persist(contractEmployee);
//Commit the transaction and close the session
t.commit();
session.close();
System.out.println("successfully persisted all the Employee records");
}
}
Step 9
Run the above class to check the output
Hibernate:
create table ContractEmployee (
id integer not null,
city varchar(255),
name varchar(255),
hourlyRate double precision,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table Employee2 (
id integer not null,
city varchar(255),
name varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table hibernate_sequence (
next_val bigint
)
Hibernate:
insert into hibernate_sequence values ( 1 )
Hibernate:
create table PermanentEmployee (
id integer not null,
city varchar(255),
name varchar(255),
salary double precision,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
select
next_val as id_val
from
hibernate_sequence for update
Hibernate:
update
hibernate_sequence
set
next_val= ?
where
next_val=?
Hibernate:
select
next_val as id_val
from
hibernate_sequence for update
Hibernate:
update
hibernate_sequence
set
next_val= ?
where
next_val=?
Hibernate:
select
next_val as id_val
from
hibernate_sequence for update
Hibernate:
update
hibernate_sequence
set
next_val= ?
where
next_val=?
Hibernate:
insert
into
Employee2
(city, name, id)
values
(?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
PermanentEmployee
(city, name, salary, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
ContractEmployee
(city, name, hourlyRate, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
successfully persisted all the Employee records
We can see 3 Create statements to create 3 tables are executed.
We can see 3 statements for updating the auto generated primary key for ID are executed.
3 insert statements one for each object we persisted are executed.
Check Table in MYSQL console
E:\MySql_Install\bin
Mysql –u root –p
Enter password
SELECT * FROM Employee2;
SELECT * FROM PermanentEmployee;
SELECT * FROM ContractEmployee;
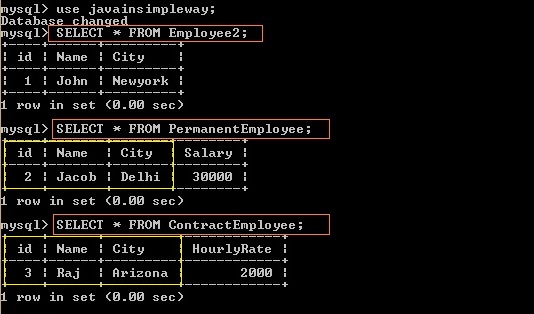
We can see that id,Name and City columns of parent class table are duplicated in each subclass tables.
Advantage
Easy to implement and avoid the NULL values getting stored in the columns
Disadvantage
Columns in parent class table are duplicated in each subclass table.
Any change in the parent class table will impact all the subclass tables.
Note :This strategy is not completely normalized as it still have duplicate columns in each subclass table.
