Cascade save-update Project in Hibernate
Let us see one end to end project for Cascade save-update
Step 1
Create hibernate project
Please refer Hibernate setup in eclipse article on how to do it.
Project structure
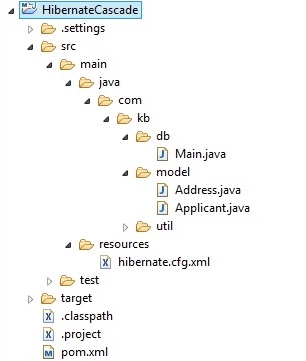
Step 2
Update pom.xml with Hibernate and Mysql dependencies
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <groupId>HibernateCascade</groupId>
- <artifactId>HibernateCascade</artifactId>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- <packaging>jar</packaging>
- <name>HibernateCascade</name>
- <url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
- <properties>
- <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>junit</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
- <version>3.8.1</version>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
- <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
- <version>5.2.6.Final</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>mysql</groupId>
- <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
- <version>6.0.5</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- </project>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>HibernateCascade</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateCascade</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>HibernateCascade</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Step 3
Create Applicant class
- package com.kb.model;
- import java.util.Set;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
- import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
- import javax.persistence.Id;
- import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- import org.hibernate.annotations.Cascade;
- import org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType;
- @Entity
- @Table(name="Applicant")
- public class Applicant {
- @Id
- @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
- @Column(name = "Applicant_Id")
- private int applicantId;
- @Column(name = "FirstName")
- private String firstName;
- @Column(name = "LastName")
- private String lastName;
- @Column(name = "Age")
- private int age;
- @Column(name = "Education")
- private String education;
- @OneToMany(mappedBy="applicant")
- @Cascade(CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE)
- private Set<Address> addresses;h
- public int getApplicantId() {
- return applicantId;
- }
- public void setApplicantId(int applicantId) {
- this.applicantId = applicantId;
- }
- public String getFirstName() {
- return firstName;
- }
- public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
- this.firstName = firstName;
- }
- public String getLastName() {
- return lastName;
- }
- public void setLastName(String lastName) {
- this.lastName = lastName;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getEducation() {
- return education;
- }
- public void setEducation(String education) {
- this.education = education;
- }
- public Set<Address> getAddresses() {
- return addresses;
- }
- public void setAddresses(Set<Address> addresses) {
- this.addresses = addresses;
- }
- }
package com.kb.model;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cascade;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType;
@Entity
@Table(name="Applicant")
public class Applicant {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
@Column(name = "Applicant_Id")
private int applicantId;
@Column(name = "FirstName")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "LastName")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "Age")
private int age;
@Column(name = "Education")
private String education;
@OneToMany(mappedBy="applicant")
@Cascade(CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE)
private Set<Address> addresses;h
public int getApplicantId() {
return applicantId;
}
public void setApplicantId(int applicantId) {
this.applicantId = applicantId;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEducation() {
return education;
}
public void setEducation(String education) {
this.education = education;
}
public Set<Address> getAddresses() {
return addresses;
}
public void setAddresses(Set<Address> addresses) {
this.addresses = addresses;
}
}
We can see that we have added Set< Address> in Applicant class to maintain OneToMany relation.
@Cascade(CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE) – is used to instruct Hibernate to use Cascade on mapped entity(Address) when Save or Update is performed on owner entity(Applicant).
It means whenever we save or update Applicant, its associated Address objects will also be saved automatically.
Step 4
Create Address class
- package com.kb.model;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
- import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
- import javax.persistence.Id;
- import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
- import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- @Entity
- @Table(name="Address")
- public class Address {
- @Id
- @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
- @Column(name = "Address_Id")
- private int addressId;
- @Column(name = "Street")
- private String street;
- @Column(name = "City")
- private String city;
- @Column(name = "Zipcode")
- private String zipcode;
- @ManyToOne
- @JoinColumn(name="Applicant_Id")
- private Applicant applicant;
- public int getAddressId() {
- return addressId;
- }
- public void setAddressId(int addressId) {
- this.addressId = addressId;
- }
- public String getStreet() {
- return street;
- }
- public void setStreet(String street) {
- this.street = street;
- }
- public String getCity() {
- return city;
- }
- public void setCity(String city) {
- this.city = city;
- }
- public String getZipcode() {
- return zipcode;
- }
- public void setZipcode(String zipcode) {
- this.zipcode = zipcode;
- }
- public Applicant getApplicant() {
- return applicant;
- }
- public void setApplicant(Applicant applicant) {
- this.applicant = applicant;
- }
- }
package com.kb.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="Address")
public class Address {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
@Column(name = "Address_Id")
private int addressId;
@Column(name = "Street")
private String street;
@Column(name = "City")
private String city;
@Column(name = "Zipcode")
private String zipcode;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="Applicant_Id")
private Applicant applicant;
public int getAddressId() {
return addressId;
}
public void setAddressId(int addressId) {
this.addressId = addressId;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getZipcode() {
return zipcode;
}
public void setZipcode(String zipcode) {
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
public Applicant getApplicant() {
return applicant;
}
public void setApplicant(Applicant applicant) {
this.applicant = applicant;
}
}
We can see that we have added Applicant in Address class to maintain other side of OneToMany relation which is ManyToOne.
Step 5
Create hibernate.cfg.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
- "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
- <hibernate-configuration>
- <session-factory>
- <!-- Database connection properties -->
- <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
- <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
- <property name="connection.username">root</property>
- <property name="connection.password">root</property>
- <!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
- <property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
- <!-- SQL dialect -->
- <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
- <!-- Disable the second-level cache -->
- <property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.internal.NoCacheProvider</property>
- <!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
- <property name="show_sql">true</property>
- <!-- Format the generated Sql -->
- <property name="format_sql">true</property>
- <!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update it -->
- <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
- <mapping class="com.kb.model.Applicant" />
- <mapping class="com.kb.model.Address" />
- </session-factory>
- </hibernate-configuration>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection properties -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
<property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
<!-- SQL dialect -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Disable the second-level cache -->
<property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.internal.NoCacheProvider</property>
<!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- Format the generated Sql -->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update it -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<mapping class="com.kb.model.Applicant" />
<mapping class="com.kb.model.Address" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
We have defined all the database configuration in this file
hbm2ddl.auto property is defined in the config file which helps in automatic creation of tables in the database based on the mapping.
We have also provided the mapping xml file location using < mapping > tag.
Step 6
Create Hibernate util class
- package com.kb.util;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
- public class HibernateUtil {
- private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
- private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
- try {
- // Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
- return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- // Make sure you log the exception to track it
- System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
- throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
- }
- }
- public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
- return sessionFactory;
- }
- public static void shutdown() {
- // Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
- getSessionFactory().close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Make sure you log the exception to track it
System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
public static void shutdown() {
// Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
getSessionFactory().close();
}
}
Step 7
Create main class to interact with DB
- package com.kb.db;
- import java.util.HashSet;
- import java.util.Set;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import org.hibernate.Transaction;
- import com.kb.model.Address;
- import com.kb.model.Applicant;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class Main {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- // Get session from Sesson factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- // Begin transaction
- Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
- //Create Applicant Model data
- Applicant applicant = new Applicant();
- applicant.setFirstName("John");
- applicant.setLastName("KC");
- applicant.setAge(28);
- applicant.setEducation("Graduation");
- //Create Address Model data
- Address currentAdd = new Address();
- currentAdd.setStreet("Royal road");
- currentAdd.setCity("Newyork");
- currentAdd.setZipcode("10001");
- currentAdd.setApplicant(applicant);
- Address permanentAdd = new Address();
- permanentAdd.setStreet("Manyar Road");
- permanentAdd.setCity("Sydney");
- permanentAdd.setZipcode("2060");
- permanentAdd.setApplicant(applicant);
- Set<Address> addresses = new HashSet<Address>();
- addresses.add(currentAdd);
- addresses.add(permanentAdd);
- applicant.setAddresses(addresses);
- session.save(applicant);
- // Commit the transaction and close the session
- t.commit();
- session.close();
- System.out.println("successfully persisted Applicant details");
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.kb.model.Address;
import com.kb.model.Applicant;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Sesson factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Begin transaction
Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
//Create Applicant Model data
Applicant applicant = new Applicant();
applicant.setFirstName("John");
applicant.setLastName("KC");
applicant.setAge(28);
applicant.setEducation("Graduation");
//Create Address Model data
Address currentAdd = new Address();
currentAdd.setStreet("Royal road");
currentAdd.setCity("Newyork");
currentAdd.setZipcode("10001");
currentAdd.setApplicant(applicant);
Address permanentAdd = new Address();
permanentAdd.setStreet("Manyar Road");
permanentAdd.setCity("Sydney");
permanentAdd.setZipcode("2060");
permanentAdd.setApplicant(applicant);
Set<Address> addresses = new HashSet<Address>();
addresses.add(currentAdd);
addresses.add(permanentAdd);
applicant.setAddresses(addresses);
session.save(applicant);
// Commit the transaction and close the session
t.commit();
session.close();
System.out.println("successfully persisted Applicant details");
}
}
We have added 1 Applicant and associated 2 addresses to it and saved only Applicant but Hibernate will take care of saving all addresses as we have used Cascade in the mapping.
Step 8
Run the above class to check the output
Check Table in MYSQL console
E:\MySql_Install\bin
Mysql –u root –p
Enter password
Use javainsimpleway;
Select * from Applicant;
Select * from address;
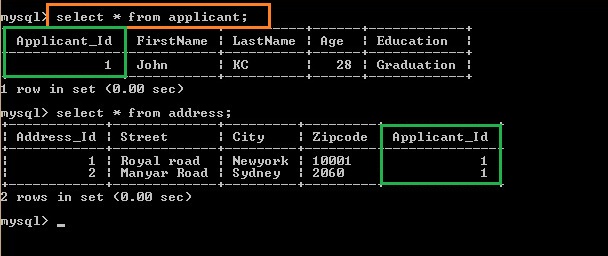
We can see that both Applcant and Address tables are persisted using Cascade.
