HQL overview in Hibernate
We have understood how to perform various operations like Insert,Update,delete and Select on single row of a table in Hibernate.
We have different methods in Hibernate like save,get,delete and update methods to perform the same
But what if we want to Select or Update or Insert all the records of a table based on some condition ?
Consider the below scenarios
What if we want to select all the records of a table ?
What if we want to join 2 tables and get the result ?
What if we want to perform aggregations on columns like avg(salary) of Employees.
Answer to all the above queries is “HQL”.
Yes Hibernate Query Language (HQL) is an object oriented query language provided by Hibernate.
HQL is very similar to SQL except that we use Class names instead of table names and attributes of a class instead of Columns of a table that makes it more close to object oriented programming.
Same thing is shown in the below figure
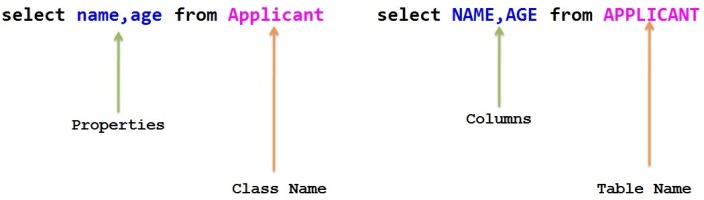
HQL SQL
HQL is case-insensitive except for java class names and attribute names.
So SeLeCT is the same as sELEct which is same as SELECT, but ‘com.kb.model.Applicant‘ is not same as ‘com.kb.model.APPLICANT‘.
HQL examples
1.Select Query examples
Select all the records of Applicant table.
- Query query = session.createQuery("from Applicant ");
- List list = query.list();
Query query = session.createQuery("from Applicant ");
List list = query.list();Where Applicant is the class name.
Equivalent SQL query
Select * from APPLICANT
Where APPLICANT is the table name
Select all the records of Applicant table whose age >30
- Query query = session.createQuery("from Applicant where age >:age ");
- query.setParameter("age", 30);
- List list = query.list();.
Query query = session.createQuery("from Applicant where age >:age ");
query.setParameter("age", 30);
List list = query.list();.Where Applicant is the class name and age is the attribute name inside Applicant class.
Equivalent SQL query
Select * from APPLICANT where AGE >30
Where APPLICANT is the table name and AGE is the column name.
Select specific columns of Applicant table
- Query query = session.createQuery("select a.name,a.age from Applicant a");
- List<Object[]> applicants= (List<Object[]>)query.list();
Query query = session.createQuery("select a.name,a.age from Applicant a");
List<Object[]> applicants= (List<Object[]>)query.list();Where Applicant is the class name , age and name are the attribute names inside Applicant class
Equivalent SQL query
select a.NAME,a.AGE from APPLICANT a
Where APPLICANT is the table name ,AGE and NAME are the column names in APPLICANT table.
2. Update Query example
- Query query = session.createQuery("update Applicant set age =:age where id=:id");
- query.setParameter("age", 30);
- query.setParameter("id", 1);
- int result = query.executeUpdate();
Query query = session.createQuery("update Applicant set age =:age where id=:id");
query.setParameter("age", 30);
query.setParameter("id", 1);
int result = query.executeUpdate();Where Applicant is the class name ,id and age are the attribute names inside Applicant class.
Equivalent SQL query
update APPLICANT set AGE =30 where ID=1
Where APPLICANT is the table name and AGE and ID are the column names
3. Delete Query example
- Query query = session.createQuery("delete from Applicant where id=:id");
- query.setParameter("id", 1);
- int result = query.executeUpdate();
Query query = session.createQuery("delete from Applicant where id=:id");
query.setParameter("id", 1);
int result = query.executeUpdate();Where Applicant is the class name ,id is the attribute name inside Applicant class.
Equivalent SQL query
Delete from APPLICANT where ID=1
Where APPLICANT is the table name and ID is the column name
4.Insert Query example
HQL INSERT can not be used to insert the records directly but it can be used to insert the records retrieved from another entity using Select statement.
So “Insert into … values(…..)” is not supported in HQL as it supports in SQL.
We need to use Insert but with Select.
- Query query = session.createQuery("insert into ApplicantBackup(id,name,age) select id,name,age from Applicant");
- int result = query.executeUpdate();
Query query = session.createQuery("insert into ApplicantBackup(id,name,age) select id,name,age from Applicant");
int result = query.executeUpdate();Where Applicant and ApplicantBackup are the class names
id,name and age are the attribute names inside Applicant and ApplicantBackup classes.
Equivalent SQL query
Insert into APPLICANT_BACKUP(ID,NAME,AGE) values(1,”john”,30);
In SQL we can directly do insert records with values without using Select, Where APPLICANT_BACKUP is the table name and ID,NAME and AGE are the column names
Note: The query.executeUpdate() method returns number of records inserted, updated or deleted.
5.Aggregate Query examples
select count(*) from Applicant
select avg(age) from Applicant
select max(age) from Applicant
select min(age) from Applicant
Where Applicant is the class name and age is the attribute name inside Applicant class
Advantages of HQL
We know the benefit of Java being platform independent , similary HQL is database independent.
It means queries written using HQL syntax will be able to execute in all the Databases without any modification in it.
HQL supports object oriented features like Inheritance, polymorphism, Associations(Relation ships) using which we can perform complex queries using Join
HQL also supports DDL operations like Insert,update along with select operation.
HQL syntax is very similar to SQL and hence learning HQL does not require huge effort if you know SQL already.
HQL can be used to perform bulk operations like selecting all the records of a Table or updating all records of a table etc.
HQL also supports query parameters to set the values dynamically.
Note:
Apart from HQL, Hibernate also supports native SQL queries using org.hibernate.SQLQuery interface we just need to call createSQLQuery() method of Session interface to use it.
