Cascades in Hibernate – overview
Let us understand Cascades in Hibernate with examples
In previous articles, we have understood about Association or Mapping between entities like One To One, One To Many and Many to Many.
In these associations, one entity will be the relationship owner and other one is just a mapped entity.
We want to save mapped entity automatically without writing any code whenever the relationship owner entity is saved.
To achieve this, we need to use Cascade in Hibernate mapping.
What is Cascade ?
Cascade is the feature provided by hibernate to automatically manage the state of mapped entity whenever the state of its relationship owner entity is affected.
In other words,
When relationship owner is saved,then associated mapped entity should also be saved and when relationship owner is deleted, associated mapped entity should also be deleted etc.
Various Cascade operations supported in Hibernate
none (default)
save
update
save-update
delete
delete-orphan
all
Let us understand How cascade is used in Hibernate with One to Many relation
We can use Cascade for all types of relation(One to One,One to Many and Many to Many)
Consider the relation between Applicant and Address
One applicant will have many addresses like Permanent and Current address
Relation looks as below
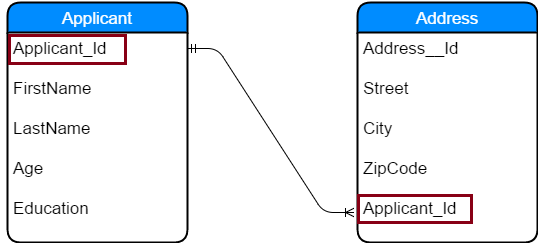
As shown in the above ER diagram,Relation between Applicant and Address is One To Many.
Address_Id is the primary key for Address table
Applicant_Id is the primary key for Applicant table
We can see that Applicant_Id which is the primary key at One side(Applicant) has become the Foreign key on the Many side(Address).
In this relation, We will make Applicant as the relation owner.
Whenever we save or update the Applicant entity , its related entity Address should also be affected automatically.
Suppose we create one Applicant object and 2 address objects and associate these 2 address objects to Applicant object
Now if we save Applicant object ,corresponding 2 Address objects should also be saved in DB.
This way we are cascading the operation performed on Owner entity to the related entity.
Cascade is supported in both XML and annotation mapping
Cascade with XML
We just need to declare the cascade with required options in the associated entity as below
applicant.hbm.xml
- <set name="addresses" table="Address"
- inverse="true" lazy="true" fetch="select" cascade="save-update, delete">
- <key>
- <column name="Applicant_Id" not-null="true" />
- </key>
- <one-to-many class="Address" />
- </set>
<set name="addresses" table="Address"
inverse="true" lazy="true" fetch="select" cascade="save-update, delete">
<key>
<column name="Applicant_Id" not-null="true" />
</key>
<one-to-many class="Address" />
</set>
Cascade with Annotation
We just need to declare the cascade with required options in the associated entity using @Cascade annotation as below.
Applicant.java
- @OneToMany(mappedBy="applicant")
- @Cascade({CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE, CascadeType.DELETE})
- private Set<Address> addresses;
@OneToMany(mappedBy="applicant")
@Cascade({CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE, CascadeType.DELETE})
private Set<Address> addresses;CascadeType is used to specify the type of Cascade.

Goo article..