Get vs Load in Hibernate with example
- 9th May 2017
- 0
- 13461
- difference between load and get in hibernate explain the difference between get and load methods in hibernate get method in hibernate is eager loading? load and get differences with an example load and get methods in hibernate load method in hibernate is lazy loading ? major difference between load and get in hibernate what is the difference between get and load methods in hibernate
Let us understand about GET and LOAD methods in Hibernate
The most widely asked and popular question in Hibernate is “Difference between Get and Load methods”.
Most of the developers use these methods alternatively but there is a substantial difference between these methods and one should use the right method in right situation.
Session.get() and session.load() methods are declared in session.
End use of both the methods is to retrieve the object(single row) from the DB.
Lets understand these 2 methods in detail and also their differences and when to use them
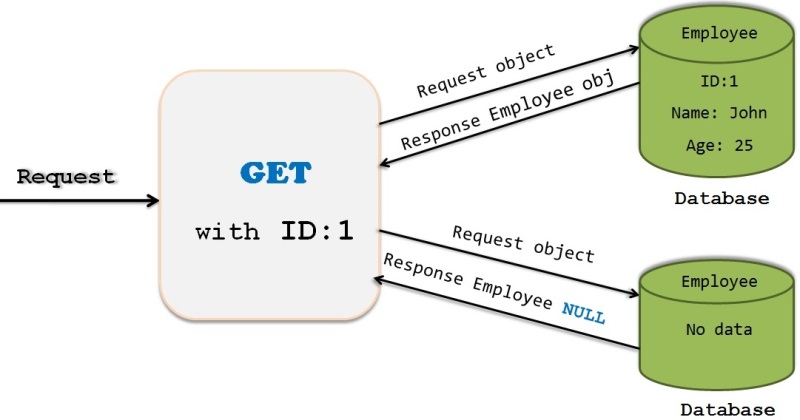
Get:
When we use session.get() method, it will hit the DB immediately and returns the real object from DB.
If there is no row corresponding to requested identifier exists , it will return NULL.
 .
.
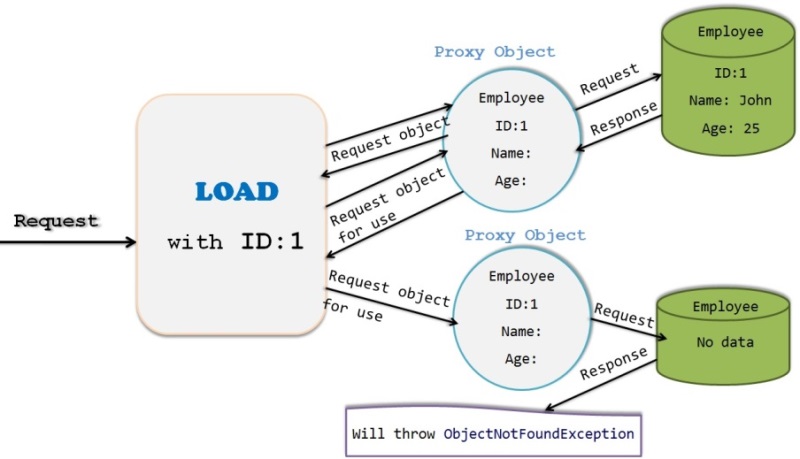
Load:
When we use session.load() method, it will always return a proxy object without hitting the DB.
Proxy object is a temporary object which does not have any values assigned to it except primary key or identifier value.
If there is no row corresponding to requested identifier exists , then it will throw “ObjectNotFoundException”.
Let us implement the same and test it through example
Step 1
Create hibernate project
Please refer Hibernate setup in eclipse article on how to do it.
Project structure
Step 2
Update pom.xml with Hibernate and Mysql dependencies
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <groupId>HibernateMergeUpdate</groupId>
- <artifactId>HibernateMergeUpdate</artifactId>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- <packaging>jar</packaging>
- <name>HibernateMergeUpdate</name>
- <url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
- <properties>
- <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>junit</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
- <version>3.8.1</version>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
- <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
- <version>5.2.6.Final</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>mysql</groupId>
- <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
- <version>6.0.5</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- </project>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>HibernateMergeUpdate</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateMergeUpdate</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>HibernateMergeUpdate</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Step 3
Create Employee class
- package com.kb.model;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
- import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
- import javax.persistence.Id;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- @Entity
- @Table(name="Employee")
- public class Employee {
- @Id
- @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
- @Column(name = "Employee_Id")
- private int employeeId;
- @Column(name = "FirstName")
- private String firstName;
- @Column(name = "LastName")
- private String lastName;
- @Column(name = "Age")
- private int age;
- @Column(name = "Education")
- private String education;
- @Column(name = "Salary")
- private int salary;
- public int getEmployeeId() {
- return employeeId;
- }
- public void setEmployeeId(int employeeId) {
- this.employeeId = employeeId;
- }
- public String getFirstName() {
- return firstName;
- }
- public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
- this.firstName = firstName;
- }
- public String getLastName() {
- return lastName;
- }
- public void setLastName(String lastName) {
- this.lastName = lastName;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getEducation() {
- return education;
- }
- public void setEducation(String education) {
- this.education = education;
- }
- public int getSalary() {
- return salary;
- }
- public void setSalary(int salary) {
- this.salary = salary;
- }
- }
package com.kb.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="Employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
@Column(name = "Employee_Id")
private int employeeId;
@Column(name = "FirstName")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "LastName")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "Age")
private int age;
@Column(name = "Education")
private String education;
@Column(name = "Salary")
private int salary;
public int getEmployeeId() {
return employeeId;
}
public void setEmployeeId(int employeeId) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEducation() {
return education;
}
public void setEducation(String education) {
this.education = education;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
We have specified Primary key as employeeId and generator class as “sequence” for automatic primary key generation.
Step 4
Create hibernate.cfg.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
- "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
- <hibernate-configuration>
- <session-factory>
- <!-- Database connection properties -->
- <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
- <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
- <property name="connection.username">root</property>
- <property name="connection.password">root</property>
- <!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
- <property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
- <!-- SQL dialect -->
- <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
- <!-- Disable the second-level cache -->
- <property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.internal.NoCacheProvider</property>
- <!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
- <property name="show_sql">true</property>
- <!-- Format the generated Sql -->
- <property name="format_sql">true</property>
- <!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update
- it -->
- <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
- <mapping class="com.kb.model.Employee" />
- </session-factory>
- </hibernate-configuration>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection properties -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
<property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
<!-- SQL dialect -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Disable the second-level cache -->
<property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.internal.NoCacheProvider</property>
<!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- Format the generated Sql -->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update
it -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<mapping class="com.kb.model.Employee" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
We have defined all the database configuration in this file
hbm2ddl.auto property is defined in the config file which helps in automatic creation of tables in the database based on the mapping.
We have also provided the mapping class name using “mapping” tag.
Step 5
Create Hibernate util class
- package com.kb.util;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
- public class HibernateUtil {
- private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
- private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
- try {
- // Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
- return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- // Make sure you log the exception to track it
- System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
- throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
- }
- }
- public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
- return sessionFactory;
- }
- public static void shutdown() {
- // Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
- getSessionFactory().close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Make sure you log the exception to track it
System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
public static void shutdown() {
// Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
getSessionFactory().close();
}
}
Step 6
Create PopulateData.java file to Populate Employee Table with initial data
- package com.kb.db;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import org.hibernate.Transaction;
- import com.kb.model.Employee;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class PopulateData {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- // Get session from Sesson factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- // Begin transaction
- Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
- //Create Employee data
- Employee employee1 = new Employee();
- employee1.setFirstName("John");
- employee1.setLastName("KC");
- employee1.setAge(28);
- employee1.setEducation("PG");
- employee1.setSalary(25000);
- Employee employee2 = new Employee();
- employee2.setFirstName("Jacob");
- employee2.setLastName("JC");
- employee2.setAge(30);
- employee2.setEducation("PG");
- employee2.setSalary(30000);
- Employee employee3 = new Employee();
- employee3.setFirstName("Martin");
- employee3.setLastName("A");
- employee3.setAge(24);
- employee3.setEducation("UG");
- employee3.setSalary(20000);
- Employee employee4 = new Employee();
- employee4.setFirstName("Peter");
- employee4.setLastName("M");
- employee4.setAge(25);
- employee4.setEducation("UG");
- employee4.setSalary(22000);
- Employee employee5 = new Employee();
- employee5.setFirstName("Roshan");
- employee5.setLastName("B");
- employee5.setAge(29);
- employee5.setEducation("PG");
- employee5.setSalary(45000);
- session.save(employee1);
- session.save(employee2);
- session.save(employee3);
- session.save(employee4);
- session.save(employee5);
- // Commit the transaction and close the session
- t.commit();
- session.close();
- System.out.println("successfully persisted Employee details");
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class PopulateData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Sesson factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Begin transaction
Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
//Create Employee data
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setFirstName("John");
employee1.setLastName("KC");
employee1.setAge(28);
employee1.setEducation("PG");
employee1.setSalary(25000);
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setFirstName("Jacob");
employee2.setLastName("JC");
employee2.setAge(30);
employee2.setEducation("PG");
employee2.setSalary(30000);
Employee employee3 = new Employee();
employee3.setFirstName("Martin");
employee3.setLastName("A");
employee3.setAge(24);
employee3.setEducation("UG");
employee3.setSalary(20000);
Employee employee4 = new Employee();
employee4.setFirstName("Peter");
employee4.setLastName("M");
employee4.setAge(25);
employee4.setEducation("UG");
employee4.setSalary(22000);
Employee employee5 = new Employee();
employee5.setFirstName("Roshan");
employee5.setLastName("B");
employee5.setAge(29);
employee5.setEducation("PG");
employee5.setSalary(45000);
session.save(employee1);
session.save(employee2);
session.save(employee3);
session.save(employee4);
session.save(employee5);
// Commit the transaction and close the session
t.commit();
session.close();
System.out.println("successfully persisted Employee details");
}
}
In this class, we are persisting 5 Employee records
Step 7
Lets Create Main class to perform Get and Load operations
Create GetExample.java
- package com.kb.db;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import com.kb.model.Employee;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class GetExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- // Get session from Session factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- // Get the Employee details whose Id is 1
- System.out.println("Calling Session.get() method");
- session.get(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
- session.close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class GetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Session factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Get the Employee details whose Id is 1
System.out.println("Calling Session.get() method");
session.get(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
session.close();
}
}
In this program, we are calling get() method to retrieve the Employee record, since get() method does not use Proxy ,query will be fired immediately to retrieve the record.
Create LoadExample.java
- package com.kb.db;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import com.kb.model.Employee;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class LoadExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- // Get session from Session factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- // Load the Employee details whose Id is 1
- System.out.println("Calling Session.load() method");
- session.load(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
- session.close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class LoadExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Session factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Load the Employee details whose Id is 1
System.out.println("Calling Session.load() method");
session.load(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
session.close();
}
}
In this program, we are calling load() method to retrieve the Employee record, since load() method uses Proxy ,query will not be fired to retrieve the data from DB.
If we use this object , then only query will be fired to DB.
Create GetExample1.java
- package com.kb.db;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import com.kb.model.Employee;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class GetExample1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- // Get session from Session factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- // Get the Employee details whose Id is 1
- System.out.println("Calling Session.get() method");
- Employee employee = (Employee)session.get(Employee.class, new
- Integer(10));
- System.out.println("Employee Obj --> "+employee);
- session.close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class GetExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Session factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Get the Employee details whose Id is 1
System.out.println("Calling Session.get() method");
Employee employee = (Employee)session.get(Employee.class, new
Integer(10));
System.out.println("Employee Obj --> "+employee);
session.close();
}
}
In this program, we are calling get() method to retrieve the Employee record whose Id is 10, but in our DB , there is no such record exists.
So get() method returns null.
Create LoadExample1.java
- package com.kb.db;
- import org.hibernate.Session;
- import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
- import com.kb.model.Employee;
- import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
- public class LoadExample1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
- SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
- // Get session from Session factory
- Session session = sf.openSession();
- // Load the Employee details whose Id is 1
- System.out.println("Calling Session.load() method");
- Employee employee = session.load(Employee.class, new Integer(10));
- System.out.println("Employee Obj --> "+employee);
- session.close();
- }
- }
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class LoadExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Session factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Load the Employee details whose Id is 1
System.out.println("Calling Session.load() method");
Employee employee = session.load(Employee.class, new Integer(10));
System.out.println("Employee Obj --> "+employee);
session.close();
}
}
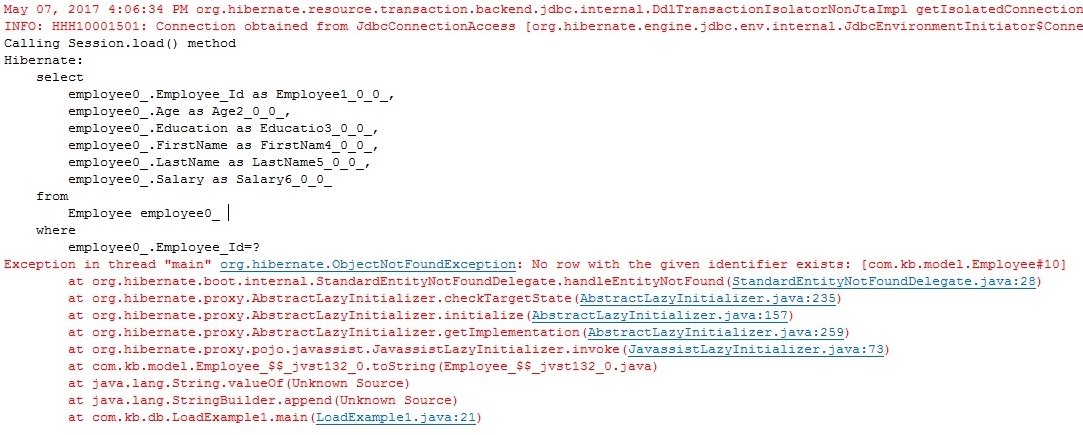
In this program, we are calling load() method to retrieve the Employee record whose Id is 10, but in our DB , there is no such record exists.
So load() method throws below exception
org.hibernate.ObjectNotFoundException: No row with the given identifier exists:
Step 8
Run PopulateData.java class to create the initial data
Step 9
Check the output in MYSQL DB
E:\MySql_Install\bin
Mysql –u root –p
Enter password
Use javainsimpleway;
Select * from Employee;
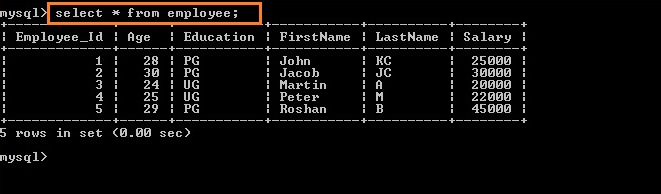
We can see that Emploeyee table has 5 records.
Step 10
Run GetExample.java
Output

Step 11
Run LoadExample.java
Output
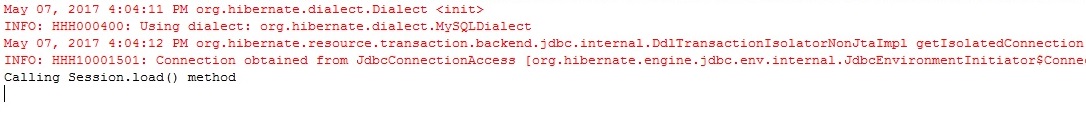
Step 12
Run GetExample1.java
Output
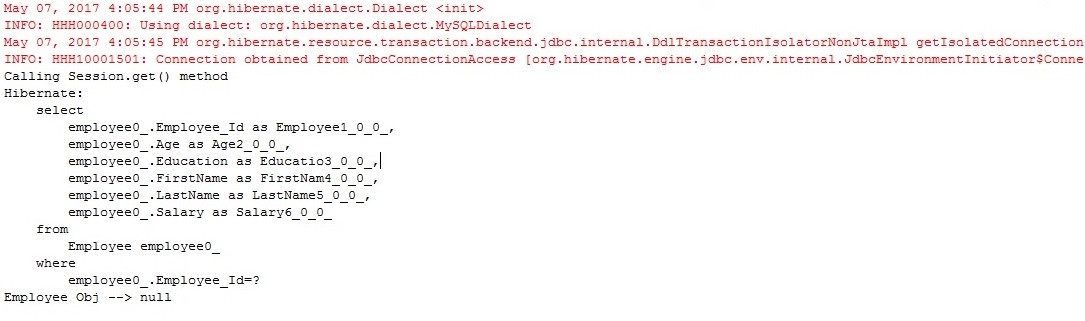
Step 13
Run LoadExample1.java
Output
Note:
Load() method fires query to DB only when the object is used by the application, just like Lazy loading. Get() method fires the query immediately to DB , just like eager loading.
