Secondary cache in Hibernate
Let us understand Secondary cache in Hibernate
Secondary cache is associated with the SessionFactory and hence its available to the entire application.
So objects kept in the secondary cache are available across multiple sessions.
Once the session factory is closed, secondary cache is cleared.
How secondary cache works ?
Whenever we try to load an entity , Hibernate first looks at a primary cache associated with a particular session.
If cached entity is found in the primary cache itself then it will be returned.
If requested entity is not found in primary cache,then hibernate looks at the second level cache.
If requested entity is found in second level cache,then it will be returned.
If requested entity is not found in secondary cache then database call is made to get the entity and it will be kept in both primary and secondary cache and then it will be returned.
How to enable secondary cache ?
We just need to follow 3 simple steps to enable secondary cache.
1) Add below configuration setting in hibernate.cfg.xml file
< property name=”cache.provider_class” >org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider< /property >
< property name=”hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache” >true< /property >
2) Add cache usage setting in hbm file or annotated class as below
XML file – < cache usage="read-only" / >
Annotated class – @Cache(usage=CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_ONLY, region=”employeeCache”)
3) Create ehcache.xml file to configure the cache region
Create hibernate project Please refer Hibernate setup in eclipse article on how to do it. Update pom.xml with required dependnecies Create the Employee class @Cache(usage=CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_ONLY, region=”employeeCache”) Region specified is “employeeCache” which has to be defined in the cache config file(ehcache.xml) Create hibernate.cfg.xml file
Create ehcache configuration file ehcache.xml < diskStore path=”java.io.tmpdir” / > but in the above file, we have stored in specific folder “cache” in C drive, for this we have used < diskStore > tag. We have defined our cache name as “employeeCache” It is a mandatory configuration, which is used when an Object needs to be cached and there are no caching regions defined. cache name=”employeeCache” : This is used to define the cache region and its configuration. we don’t need to define timeToIdleSeconds and timeToLiveSeconds attributes explicitely. If we specify eternal=”false” then we need to define timeToIdleSeconds and timeToLiveSeconds attributes as we defined above. timeToIdleSeconds : It defines that how many seconds object can be idle in the second level cache. timeToLiveSeconds : It defines that how many seconds object can be stored in the second level cache no matter whether it is idle or not. memoryStoreEvictionPolicy : It is used to evict the elements from the cache memory. LFU specifies the Least frequently used element will be evicted first. Persistent strategy “localTempSwap” strategy allows the cache to overflow to disk during cache operation, providing an extra tier for cache storage Create hibernate utility class
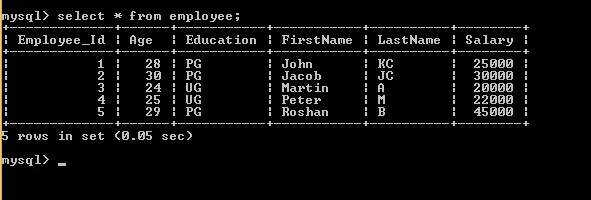
Populate the data in DB
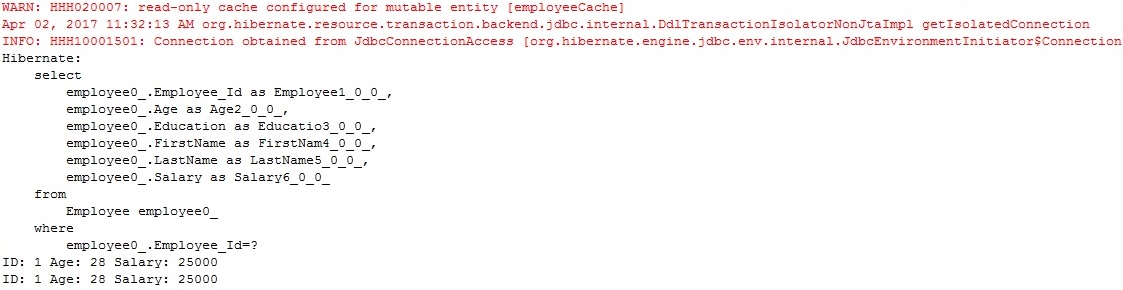
Check the output and queries executed Create test class for testing secondary cache Check the output and queries executed We can see that query to load the object is executed only once even though we are loading the object twice using different sessions. This is because object is first loaded from DB and then stored in secondary cache and hence all subsequent sessions using same session factory will load it from secondary cache.
Create test class for clearing secondary cache using evict() method SecondaryCacheEvict.java
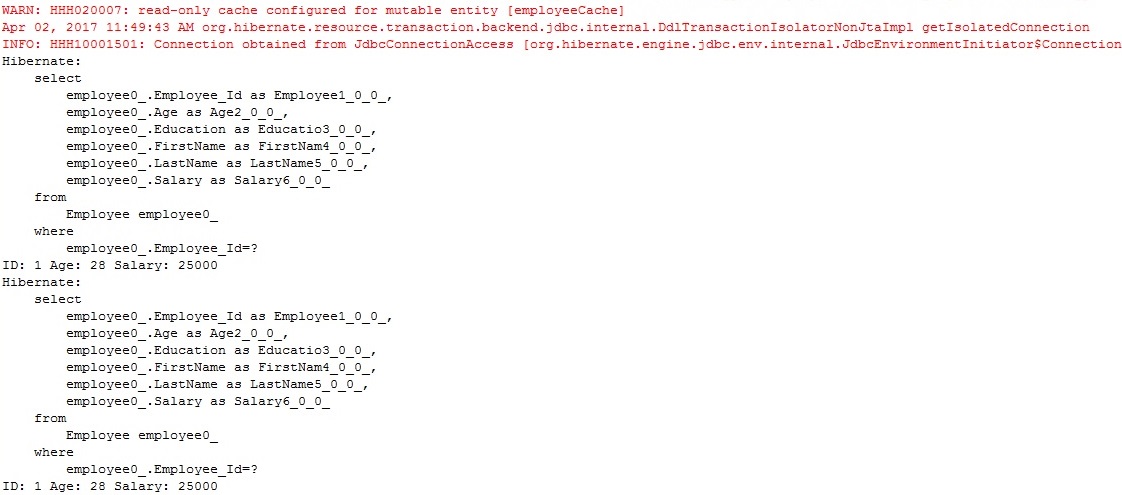
Check the output and queries executed We can see that the same object is loaded twice from DB even though we have configured second level cache. This is because we are evicting the secondary cache before loading it second time. If we change the data directly in database then secondary cache will not have this latest data updated immediately, however after “timeToLiveSeconds” defined for the cache region , latest data will be updated in the secondary cache. If we want to immediately update the latest data to secondary cache,we can invalidate the whole secondary cache using above code explained in Step 11 and Hibernate will update the cache data once again with a latest data in DB.
Let us see complete project on secondary cache using “Ehcache”
There are many other Cache providers but EhCache is one of the most widely used cache provider with Hibernate.Step 1
Project structure
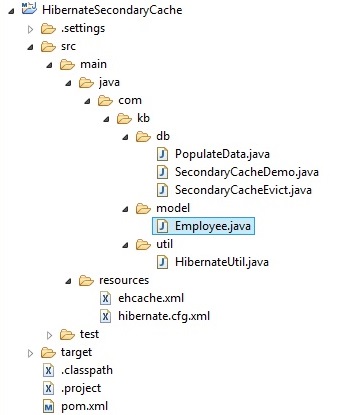
Step 2
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>HibernateSecondaryCache</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateSecondaryCache</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>HibernateSecondaryCache</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.sf.ehcache/ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>5.2.9.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
We have added dependencies for EhCache, hibernate and Mysql DB.Step 3
package com.kb.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
@Entity
@Table(name="Employee")
@Cache(usage=CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_ONLY, region="employeeCache")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE)
@Column(name = "Employee_Id")
private int employeeId;
@Column(name = "FirstName")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "LastName")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "Age")
private int age;
@Column(name = "Education")
private String education;
@Column(name = "Salary")
private int salary;
public int getEmployeeId() {
return employeeId;
}
public void setEmployeeId(int employeeId) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEducation() {
return education;
}
public void setEducation(String education) {
this.education = education;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
We have enabled cache at the entity level using below annotationStep 4
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection properties -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/javainsimpleway</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<!-- JDBC connection pool (using the built-in) -->
<property name="connection.pool_size">100</property>
<!-- SQL dialect -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Enable the second-level cache -->
<property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- Format the generated Sql -->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!-- Dont Drop and re-create the database schema on startup,Just update
it -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<mapping class="com.kb.model.Employee" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>Step 5
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="true"
monitoring="autodetect" dynamicConfig="true">
<diskStore path="c:\\cache" />
<!-- default cache -->
<defaultCache maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000" eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="30"
maxEntriesLocalDisk="10000000" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" statistics="true">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap" />
</defaultCache>
<cache name="employeeCache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000"
maxEntriesLocalDisk="1000"
eternal="false"
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="20"
timeToIdleSeconds="300" timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU"
transactionalMode="off">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap" />
</cache>
</ehcache>
By default, Ehcache stores the cached files in temp folder. Which can be configured as belowdefaultCache
eternal=true/false
If we specify eternal=”true”, hibernate will internally define the idle time and time span of cache region.
Step 6
package com.kb.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Make sure you log the exception to track it
System.err.println("SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
public static void shutdown() {
// Optional but can be used to Close caches and connection pools
getSessionFactory().close();
}
}Step 7
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class PopulateData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Sesson factory
Session session = sf.openSession();
// Begin transaction
Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
//Create Employee data
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setFirstName("John");
employee1.setLastName("KC");
employee1.setAge(28);
employee1.setEducation("PG");
employee1.setSalary(25000);
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setFirstName("Jacob");
employee2.setLastName("JC");
employee2.setAge(30);
employee2.setEducation("PG");
employee2.setSalary(30000);
Employee employee3 = new Employee();
employee3.setFirstName("Martin");
employee3.setLastName("A");
employee3.setAge(24);
employee3.setEducation("UG");
employee3.setSalary(20000);
Employee employee4 = new Employee();
employee4.setFirstName("Peter");
employee4.setLastName("M");
employee4.setAge(25);
employee4.setEducation("UG");
employee4.setSalary(22000);
Employee employee5 = new Employee();
employee5.setFirstName("Roshan");
employee5.setLastName("B");
employee5.setAge(29);
employee5.setEducation("PG");
employee5.setSalary(45000);
session.save(employee1);
session.save(employee2);
session.save(employee3);
session.save(employee4);
session.save(employee5);
// Commit the transaction and close the session
t.commit();
session.close();
System.out.println("successfully persisted Employee details");
}
}Step 8
Step 9
package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class SecondaryCacheDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Session factory
Session session1 = sf.openSession();
// Load the Employee details whose Id is 1
Employee employee = (Employee) session1.load(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
displayEmployeeDetails(employee);
// Create a new Session
Session session2 = sf.openSession();
// Load the same Employee again with new Session
employee = (Employee) session2.load(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
displayEmployeeDetails(employee);
session1.close();
session2.close();
}
private static void displayEmployeeDetails(Employee employee) {
System.out.println( "ID: " + employee.getEmployeeId() + " Age: " + employee.getAge() + " Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
}
We have created 2 separate session objects and loading the same object using 2 different sessions to check whether its loading the object from secondary cache or not.Step 10
Step 11
How to invalidate or evict the second level cache ?
We can use sessionFactory.getCache().evictAll(); method to invalidate the secondary cache at any point of time.package com.kb.db;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.kb.model.Employee;
import com.kb.util.HibernateUtil;
public class SecondaryCacheEvict {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get session factory using Hibernate Util class
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
// Get session from Session factory
Session session1 = sf.openSession();
// Load the Employee details whose Id is 1
Employee employee = (Employee) session1.load(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
displayEmployeeDetails(employee);
session1.close();
sf.getCache().evictAll();
Session session2 = sf.openSession();
// Load the same Employee again within the same Session but after evict
employee = (Employee) session2.load(Employee.class, new Integer(1));
displayEmployeeDetails(employee);
session2.close();
}
private static void displayEmployeeDetails(Employee employee) {
System.out.println("ID: " + employee.getEmployeeId() + " Age: " + employee.getAge() + " Salary: " +
employee.getSalary());
}
}Step 12
How secondary cache will be aware of any direct database changes ?
