Variables and Data types
Variables in java are the graceful representation of memory address of the value.
Ex: int x =3;
Below figure shows the memory address representation of the value stored as per the above statement.
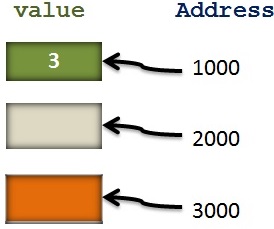
Value ‘3’ is stored at the address 1000, this 1000 can be represented in the program as some variable.
In the above case it is x, so ‘x’ is a variable.
There are different types of variables in Java.
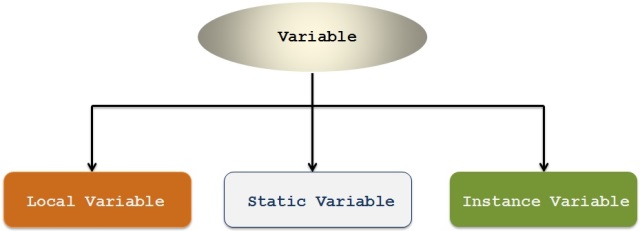
Local Variable :
A variable that is declared inside any method.
It is called local because, it is accessible only within that method.
Instance Variable :
A variable declared inside the class but not inside any method and it is not declared as static.
Static variable :
A variable declared as a ‘static’ .
Let’s see an example to understand all the variables.
- public class VariableTypes {
- int x=3;//instance variable
- static int y=4;//static variable
- public void method() {
- int z=4;//local variable
- }
- }
public class VariableTypes {
int x=3;//instance variable
static int y=4;//static variable
public void method() {
int z=4;//local variable
}
}
Datatypes in Java
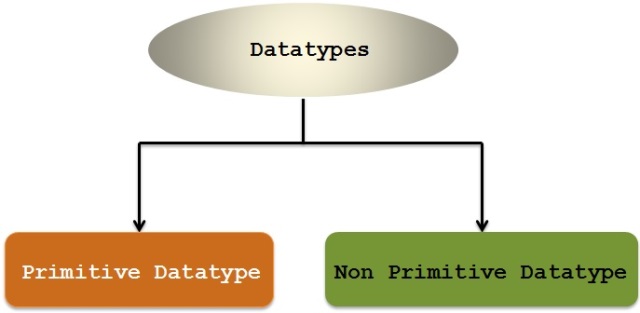
Primitive Datatype:
Are those which are predefined by the Java language and are reserved by a keyword and they will not have any class for that, they are just reserved keywords.
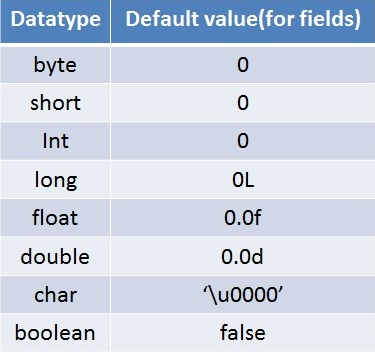
There are 8 different primitive types supported in Java
Non Primitive Datatype :
Are those which are defined with its class.
Ex:String
Note:
Custom data types like Person,Employee are also non primitive datatype.
