Inheritance in Java
Inheritance is one of the most important OOPS concepts where one class inherits or acquires the properties of another class.
The class from which the properties are inherited is called Super class or Parent class
The class which inherit the properties is called Subclass or Child class.
We use “extends” keyword to achieve the same.
The whole idea behind inheritance is “Reusability”.
We can create more specific classes by inheriting fields and methods from the Generic class.
And we can add additional fields and methods in the Subclass.
Syntax
- class Subclass-name extends Superclass-name
- {
- // fields and methods
- }
class Subclass-name extends Superclass-name
{
// fields and methods
}
Example
- Class A{
- //Fields and methods
- }
- Class B extends A{
- }
Class A{
//Fields and methods
}
Class B extends A{
}
We use “extends” keyword to inherit the properties of another class as shown above.
In the above example, class “A” is the parent class and class “B” is the subclass.
class “B” inherits the properties from class “A”.
Let us see the real-time example
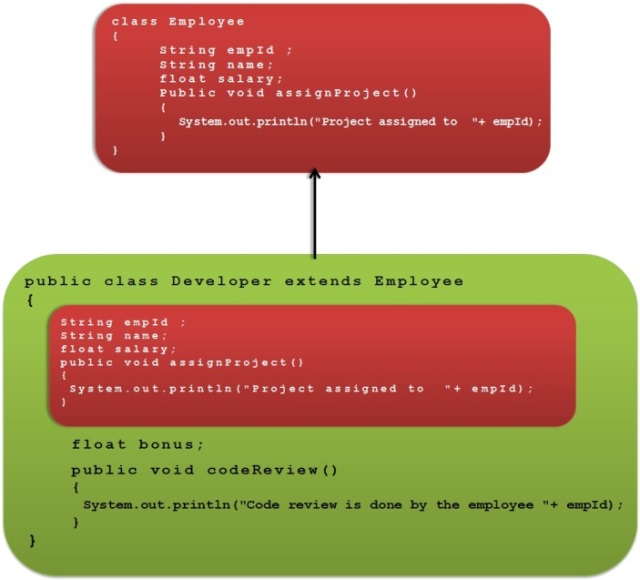
We can observe in the above diagram that Developer class is inheriting all the properties of Employee class.
Let’s achieve the same using below code
Employee.java
- package com.kb.inheritance;
- class Employee{
- String empId ;
- String name;
- float salary;
- Public void assignProject(){
- System.out.println("Project assigned to "+ empId);
- }
- }
package com.kb.inheritance;
class Employee{
String empId ;
String name;
float salary;
Public void assignProject(){
System.out.println("Project assigned to "+ empId);
}
}
Developer.java
- package com.kb.inheritance;
- public class Developer extends Employee {
- float bonus;
- Public void codeReview(){
- System.out.println("Code review is done by the employee "+ empId);
- }
- }
package com.kb.inheritance;
public class Developer extends Employee {
float bonus;
Public void codeReview(){
System.out.println("Code review is done by the employee "+ empId);
}
}
InheritanceTest.java
- package com.kb.inheritance;
- class InheritanceTest{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Developer dev = new Developer();
- dev.empId=”101”;
- dev.name=”John”;
- dev.salary=34000.5f;
- dev.bonus=20000.5f;
- System.out.println("bonus is "+dev.bonus);
- Dev.codeReview();
- }
- }
package com.kb.inheritance;
class InheritanceTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Developer dev = new Developer();
dev.empId=”101”;
dev.name=”John”;
dev.salary=34000.5f;
dev.bonus=20000.5f;
System.out.println("bonus is "+dev.bonus);
Dev.codeReview();
}
}
In the above example, we can understand that Employee is the Parent class and Developer is the subclass.
All the attributes of Employee class are inherited to Developer class and hence we don’t need to declare them again in the Developer class.

I simply wanted to write down a quick word to say thanks to you for those wonderful tips and hints you are showing on this site.