Spring Rest service – Exception handling
Exception Handling in Spring Rest service
We have seen Exception handling in Spring MVC in this and this article.
It is very similar in Spring Rest service also to handle the exception but the main difference is, In Spring MVC we will return error view page to the client where as in Spirng Rest service we need to send the error response with appropriate format so that the consumer of the Rest service will get a clear information about the response status and can proceed further.
Create a new Maven Web project in eclipse (Refer Spring MVC Hello World project for the same)
Project structure
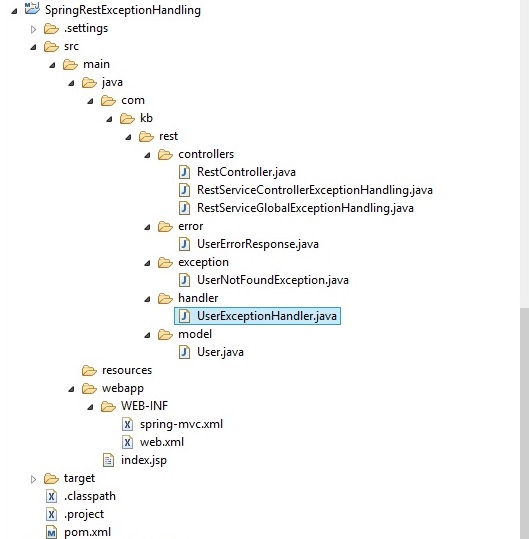
Step 1
Update pom.xml with below dependencies
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <groupId>SpringRestExceptionHandling</groupId>
- <artifactId>SpringRestExceptionHandling</artifactId>
- <packaging>war</packaging>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- <name>SpringRestExceptionHandling Maven Webapp</name>
- <url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
- <properties>
- <org.springframework.version>4.2.0.RELEASE</org.springframework.version>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>junit</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
- <version>3.8.1</version>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
- <version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
- <version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- Jackson JSON -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
- <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
- <version>2.8.5</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- <build>
- <finalName>SpringRestExceptionHandling</finalName>
- </build>
- </project>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>SpringRestExceptionHandling</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringRestExceptionHandling</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringRestExceptionHandling Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<org.springframework.version>4.2.0.RELEASE</org.springframework.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Jackson JSON -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringRestExceptionHandling</finalName>
</build>
</project>We have added dependencies for Spring web ,spring web mvc,Jackson and Junit in the above pom file.
Step 2
Update web.xml file with Dispatcher servlet
we have defined a dispatcher servlet in web.xml and mapped it by the URL pattern “/”
So just like any other servlet in web application,any request matching with the given pattern i.e “/” will be redirected to “Dispatcher servlet”.
- <web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
- xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
- http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
- <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
- <servlet>
- <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
- <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
- <init-param>
- <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
- <param-value>
- /WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml
- </param-value>
- </init-param>
- <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
- </servlet>
- <servlet-mapping>
- <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
- <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
- </servlet-mapping>
- <context-param>
- <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
- <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
- </context-param>
- <listener>
- <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
- </listener>
- </web-app>
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml
</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>We have also provided the spring configuration file name to create and load the spring beans while starting the server.
Step 3
Create a spring config file
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.2.xsd">
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.kb.rest" />
- <mvc:annotation-driven />
- </beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.2.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.kb.rest" />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
</beans>we have defined the base package as “com.kb.rest” so that anything inside this package will be eligible to become spring bean.
Step 4
Create a domain class which represents the data in JSON format
- package com.kb.rest.model;
- public class User {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- private int id;
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.model;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private int id;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}We have created a User class with id,name and age to represent the data
Step 5
Create a rest service controller class
- package com.kb.rest.controllers;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
- import com.kb.rest.model.User;
- @Controller
- @RequestMapping("/user")
- public class RestController {
- @RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public @ResponseBody User getUserForId(@PathVariable ("id") int id) {
- User user = new User();
- user.setId(id);
- user.setName("John");
- user.setAge(45);
- if(id !=1){
- throw new RuntimeException();
- }
- return user;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.controllers;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.kb.rest.model.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class RestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody User getUserForId(@PathVariable ("id") int id) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("John");
user.setAge(45);
if(id !=1){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
return user;
}
}In the above Rest service, we are throwing exception if the user id is anything other than 1 and there is no handler defined.
Step 6
Deploy the code and try to access the user with id 2
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestExceptionHandling/user/getSpecificUser/2
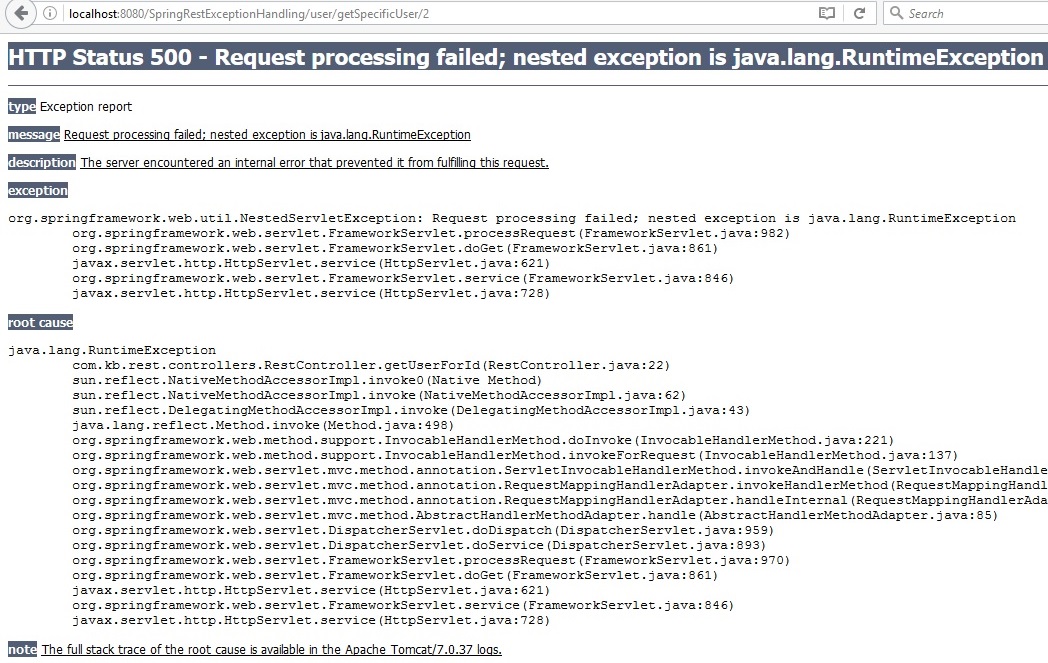
Now client does not know how to handle this exception as it does not have any information about it.
Hence we can see the exception stack trace at the client side.
Now let’s write a Rest Service which can handle the exception
Step 7
Create a custom exception class
- package com.kb.rest.exception;
- public class UserNotFoundException extends Exception {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
- private String errorMessage;
- public UserNotFoundException() {
- super();
- }
- public UserNotFoundException(String errorMessage) {
- super(errorMessage);
- this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
- }
- public String getErrorMessage() {
- return errorMessage;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.exception;
public class UserNotFoundException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String errorMessage;
public UserNotFoundException() {
super();
}
public UserNotFoundException(String errorMessage) {
super(errorMessage);
this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
}
public String getErrorMessage() {
return errorMessage;
}
}We have created a custom exception class with errorMessage property.
Step 8
Create error response class
- package com.kb.rest.error;
- public class UserErrorResponse {
- private int errorCode;
- private String errorMessage;
- public int getErrorCode() {
- return errorCode;
- }
- public void setErrorCode(int errorCode) {
- this.errorCode = errorCode;
- }
- public String getErrorMessage() {
- return errorMessage;
- }
- public void setErrorMessage(String errorMessage) {
- this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.error;
public class UserErrorResponse {
private int errorCode;
private String errorMessage;
public int getErrorCode() {
return errorCode;
}
public void setErrorCode(int errorCode) {
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public String getErrorMessage() {
return errorMessage;
}
public void setErrorMessage(String errorMessage) {
this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
}
}
There are 2 ways to handle the exception in Rest service
1) Controller based Exception handler
2) Global exception handler
1) Controller based Exception handler
In this type of Exception handling, we can write handler methods inside the controller class itself.
So to achive this , we need to
a) Define a new method inside the controller
b) Annotate this mehod with @ExceptionHandler and parameter as Exception that we have to handle
c) Handle the Exception inside this method and return the response in the required format.
Limitation of this approach is that , only those exceptions which are thrown inside this controller class can be handled.
Any exceptions thrown from outside this controller class will be left unhandled and same exception stack trace will be sent to client side.
Step 9
Create a Rest service which can have Controller based exception handling
- package com.kb.rest.controllers;
- import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
- import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
- import com.kb.rest.error.UserErrorResponse;
- import com.kb.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
- import com.kb.rest.model.User;
- @Controller
- @RequestMapping("/user/controllerExceptionHandler")
- public class RestServiceControllerExceptionHandling {
- @RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<User> getUserForId(@PathVariable("id") int id) throws UserNotFoundException {
- User user = new User();
- user.setId(id);
- user.setName("John");
- user.setAge(45);
- if (id != 1) {
- throw new UserNotFoundException("User not found");
- }
- return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
- }
- @ExceptionHandler(UserNotFoundException.class)
- public ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse> handleUserNotFoundException(Exception ex) {
- UserErrorResponse errorResponse = new UserErrorResponse();
- errorResponse.setErrorCode(HttpStatus.PRECONDITION_FAILED.value());
- errorResponse.setErrorMessage(ex.getMessage());
- return new ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse>(errorResponse, HttpStatus.OK);
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.controllers;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.kb.rest.error.UserErrorResponse;
import com.kb.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
import com.kb.rest.model.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user/controllerExceptionHandler")
public class RestServiceControllerExceptionHandling {
@RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<User> getUserForId(@PathVariable("id") int id) throws UserNotFoundException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("John");
user.setAge(45);
if (id != 1) {
throw new UserNotFoundException("User not found");
}
return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse> handleUserNotFoundException(Exception ex) {
UserErrorResponse errorResponse = new UserErrorResponse();
errorResponse.setErrorCode(HttpStatus.PRECONDITION_FAILED.value());
errorResponse.setErrorMessage(ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse>(errorResponse, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}we have defined the Rest Service with Controller Exception Handling.
we are throwing the UserNotFoundException when user id is anything other than 1.
and there is a handler method in the controller which is handling this exception and returning a response with valid error code and error message.
Step 10
Deploy the code and try to access the user with id 2
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestExceptionHandling/user/controllerExceptionHandler/getSpecificUser/2
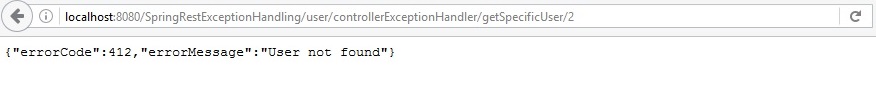
we can see that error code and error message sent to the client, Now client can easily understand the exception and proceed further.
2) Global Exception handler
In this approach , the implementation is almost similar to @ExceptionHandler approach only.
The only difference here is that , it can handle all the exceptions thrown from any of the controllers in the application.
So it is always advisable to use this approach.
It can be implemented as
a) Define a new class and annotate this class with @ControllerAdvice
b) Keep on adding new method for each exception using @ExceptionHandler annotation.
So class which is annotated with @ControllerAdvice is considered as global exception handler because methods inside it can handle the exception thrown from any controller in the application.
Step 11
Create a Rest service which throws exception in some scenario
- package com.kb.rest.controllers;
- import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
- import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
- import com.kb.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
- import com.kb.rest.model.User;
- @Controller
- @RequestMapping("/user/globalExceptionHandler")
- class RestServiceGlobalExceptionHandling {
- @RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<User> getUserForId(@PathVariable("id") int id) throws Exception {
- User user = new User();
- user.setId(id);
- user.setName("John");
- user.setAge(45);
- if (id != 1) {
- throw new UserNotFoundException("User not found");
- }
- // Intentionally throwing exception
- int ageByZero = user.getAge() / 0;
- user.setAge(ageByZero);
- return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.controllers;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.kb.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
import com.kb.rest.model.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user/globalExceptionHandler")
class RestServiceGlobalExceptionHandling {
@RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<User> getUserForId(@PathVariable("id") int id) throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("John");
user.setAge(45);
if (id != 1) {
throw new UserNotFoundException("User not found");
}
// Intentionally throwing exception
int ageByZero = user.getAge() / 0;
user.setAge(ageByZero);
return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}we have defined the Rest Service which can throw multiple exceptions.
In this service,we are throwing the UserNotFoundException when user id is anything other than 1.
We are also intentionally throwing Divide by Zero Arithmetic exception when user id is 1
Step 12
Create a global exception handler class
- package com.kb.rest.handler;
- import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
- import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
- import com.kb.rest.error.UserErrorResponse;
- import com.kb.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
- @ControllerAdvice
- public class UserExceptionHandler {
- @ExceptionHandler(UserNotFoundException.class)
- public ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse> handleUserNotFoundException(Exception ex) {
- UserErrorResponse errorResponse = new UserErrorResponse();
- errorResponse.setErrorCode(HttpStatus.PRECONDITION_FAILED.value());
- errorResponse.setErrorMessage(ex.getMessage());
- return new ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse>(errorResponse, HttpStatus.OK);
- }
- @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
- public ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse> handleGenericException(Exception ex) {
- UserErrorResponse errorResponse = new UserErrorResponse();
- errorResponse.setErrorCode(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
- errorResponse.setErrorMessage("There is some techncal issue");
- return new ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse>(errorResponse, HttpStatus.OK);
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.handler;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import com.kb.rest.error.UserErrorResponse;
import com.kb.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
@ControllerAdvice
public class UserExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse> handleUserNotFoundException(Exception ex) {
UserErrorResponse errorResponse = new UserErrorResponse();
errorResponse.setErrorCode(HttpStatus.PRECONDITION_FAILED.value());
errorResponse.setErrorMessage(ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse>(errorResponse, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse> handleGenericException(Exception ex) {
UserErrorResponse errorResponse = new UserErrorResponse();
errorResponse.setErrorCode(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
errorResponse.setErrorMessage("There is some techncal issue");
return new ResponseEntity<UserErrorResponse>(errorResponse, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}This exception handler class will handle the exceptions thrown in any of the controller
It has 2 handler methods one for handling UserNotFoundException and another one for handling Generic exception
Step 13
Deploy the code and try to access the user with id 2
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestExceptionHandling/user/globalExceptionHandler/getSpecificUser/2
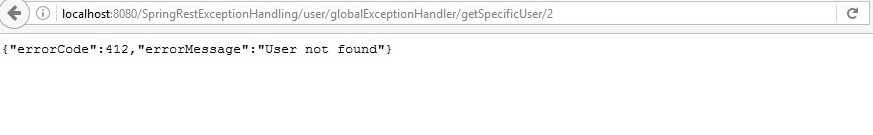
we can see that meaningful error code and error message sent to the client, Now client can easily understand the exception and proceed further.
Access the below url which will throw Divide by Zero Arithmetic exception
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestExceptionHandling/user/globalExceptionHandler/getSpecificUser/1
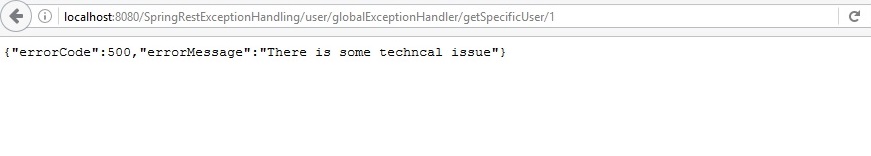
Here also we can see that meaningful error code and error message sent to the client, Now client can easily understand the exception and proceed further.

If we give give different url then which error response will come?