Spring Rest Service CRUD operations with JSON
CRUD
stands for Create,Read,Update and Delete operation
These are the most common operations that we perform in any application.

Let’s do these operations using Spring Rest service.
Requirement :
Perform CRUD operations on USER object.
We have User Domain object, we can insert User data, read the inserted data,
Update some user information and finally delete the user data.
Create a new Maven Web project in eclipse (Refer Spring MVC Hello World project for the same)
Project structure

Step 1
Update pom.xml with below dependencies
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <groupId>SpringRestCRUDJSON</groupId>
- <artifactId>SpringRestCRUDJSON</artifactId>
- <packaging>war</packaging>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- <name>SpringRestCRUDJSON Maven Webapp</name>
- <url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
- <properties>
- <org.springframework.version>4.2.0.RELEASE</org.springframework.version>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>junit</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
- <version>3.8.1</version>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
- <version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
- <version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- Jackson JSON -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
- <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
- <version>2.8.5</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- <build>
- <finalName>SpringRestCRUDJSON</finalName>
- </build>
- </project>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>SpringRestCRUDJSON</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringRestCRUDJSON</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringRestCRUDJSON Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<org.springframework.version>4.2.0.RELEASE</org.springframework.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Jackson JSON -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringRestCRUDJSON</finalName>
</build>
</project>We have added dependencies for Spring web ,spring web mvc,Jackson and Junit in the above pom file.
Step 2
Update web.xml file with Dispatcher servlet
we have defined a dispatcher servlet in web.xml and mapped it by the URL pattern “/”
So just like any other servlet in web application,any request matching with the given pattern i.e “/” will be redirected to “Dispatcher servlet”.
- <web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
- xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
- http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
- <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
- <servlet>
- <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
- <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
- <init-param>
- <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
- <param-value>
- /WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml
- </param-value>
- </init-param>
- <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
- </servlet>
- <servlet-mapping>
- <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
- <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
- </servlet-mapping>
- <context-param>
- <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
- <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
- </context-param>
- <listener>
- <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
- </listener>
- </web-app>
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml
</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>We have also provided the spring configuration file name to create and load the spring beans while starting the server.
Step 3
Create a domain class which represents the data in JSON format
We will perform CRUD operations on this object.
- package com.kb.rest.model;
- public class User {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- private int id;
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.model;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private int id;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}We have created a User class with id,name and age to represent the data
Step 4
Create the resource mapping class which will have the URL mapping methods for all our CRUD operations
- package com.kb.rest.controllers;
- import java.util.List;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
- import com.kb.rest.model.User;
- import com.kb.rest.service.UserService;
- @Controller
- @RequestMapping("/user")
- public class RestController {
- @Autowired
- private UserService userService;
- // CRUD -- CREATE operation
- @RequestMapping(value = "/create", method = RequestMethod.POST)
- public @ResponseBody User createUser(User user) {
- User userResponse = userService.createUser(user);
- return userResponse;
- }
- // CRUD -- READ operation
- @RequestMapping(value = "/getAllUsers", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public @ResponseBody List<User> getAllUsers() {
- List<User> userList = userService.getAllUsers();
- return userList;
- }
- // CRUD -- READ operation
- @RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public @ResponseBody User getUserForId(@PathVariable ("id") int id) {
- User user = userService.getUserForId(id);
- return user;
- }
- // CRUD -- UPDATE operation
- @RequestMapping(value = "/updateUser", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
- public @ResponseBody User updateUser(User user) {
- User userResponse = userService.updateUser(user);
- return userResponse;
- }
- // CRUD -- DELETE operation
- @RequestMapping(value = "/deleteUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
- public @ResponseBody User deleteeUser(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
- User userResponse = userService.deleteUser(id);
- return userResponse;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.controllers;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.kb.rest.model.User;
import com.kb.rest.service.UserService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class RestController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
// CRUD -- CREATE operation
@RequestMapping(value = "/create", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public @ResponseBody User createUser(User user) {
User userResponse = userService.createUser(user);
return userResponse;
}
// CRUD -- READ operation
@RequestMapping(value = "/getAllUsers", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody List<User> getAllUsers() {
List<User> userList = userService.getAllUsers();
return userList;
}
// CRUD -- READ operation
@RequestMapping(value = "/getSpecificUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody User getUserForId(@PathVariable ("id") int id) {
User user = userService.getUserForId(id);
return user;
}
// CRUD -- UPDATE operation
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateUser", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public @ResponseBody User updateUser(User user) {
User userResponse = userService.updateUser(user);
return userResponse;
}
// CRUD -- DELETE operation
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteUser/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public @ResponseBody User deleteeUser(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
User userResponse = userService.deleteUser(id);
return userResponse;
}
}We have created the Controller class above which will act as a Rest service in Spring.
How Spring controller acts as a Rest service ?
We have @ResponseBody before the return type of a method in method signature which indicates to Spring that ,the returned value from this method will not be a view rather it has to be read from the response body.
Hence any one can call this method with the appropriate end point
@PathVariable :
It is used to get the parameter value passed along with the URL.
Its very similar to @PathParam in JAX-RS.
@PathVariable(“id”) int id
This will get the value passed in the URL and inject it to id variable of method argument.
Possible end points for the above CRUD operations are as below
| Request Method | End point | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/getSpecificUser/3 | Get user based on ID(which is 3 in this case) |
| GET | http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/ getAllUsers | Get all the users |
| POST | http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/create | Create new User record and store it |
| PUT | http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/updateUser | Update the user object |
| DELETE | http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/deleteUser/3 | Delete the user object with id 3 |
We can also use @RestController directly instead of @Controller, in that case we don’t need to use @ResponseBody in each method.
@RestController=@Controller + @ResponseBody
Note: @RestController is supported in Spring 4 and above
Step 5
Create the business service class
- package com.kb.rest.service;
- import java.util.List;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
- import com.kb.rest.dao.UserDAO;
- import com.kb.rest.model.User;
- @Service
- public class UserService {
- @Autowired
- private UserDAO userDao;
- public List<User> getAllUsers() {
- List<User> userList = userDao.getAllUsers();
- return userList;
- }
- public User getUserForId(int id) {
- User user = userDao.getUserForId(id);
- return user;
- }
- public User createUser(User user) {
- User userResponse = userDao.createUser(user);
- return userResponse;
- }
- public User updateUser(User user) {
- User userResponse = userDao.updateUser(user);
- return userResponse;
- }
- public User deleteUser(int id) {
- User userResponse = userDao.deleteUser(id);
- return userResponse;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.kb.rest.dao.UserDAO;
import com.kb.rest.model.User;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDAO userDao;
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
List<User> userList = userDao.getAllUsers();
return userList;
}
public User getUserForId(int id) {
User user = userDao.getUserForId(id);
return user;
}
public User createUser(User user) {
User userResponse = userDao.createUser(user);
return userResponse;
}
public User updateUser(User user) {
User userResponse = userDao.updateUser(user);
return userResponse;
}
public User deleteUser(int id) {
User userResponse = userDao.deleteUser(id);
return userResponse;
}
}We have defined 5 methods in the above class
getAllUsers() – This method is used to get all the users, helps to serve GET request
getUserForId(String id) – This method is used to get the user details for a specific user,helps to serve the GET request for a specific user
createUser(User user) – This method is used to insert the new user details,helps to serve the POST request
updateUser(User user) – This method is used to update the user details,helps to serve the PUT request
deleteUser(String id) – This method is used to delete the user details,helps to serve the DELETE request
Step 6
Create the DAO class
- package com.kb.rest.dao;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
- import com.kb.rest.model.User;
- //Just to avoid DB calls in this example, Assume below data is interacting with DB
- @Repository
- public class UserDAO {
- static HashMap<Integer, User> usersMap = new HashMap<Integer, User>();
- public UserDAO() {
- User user1 = new User();
- user1.setId(1);
- user1.setAge(20);
- user1.setName("raj");
- User user2 = new User();
- user2.setId(2);
- user2.setAge(21);
- user2.setName("ram");
- usersMap.put(1, user1);
- usersMap.put(2, user2);
- }
- public List<User> getAllUsers() {
- List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>(usersMap.values());
- return userList;
- }
- public User getUserForId(int id) {
- User user = usersMap.get(id);
- return user;
- }
- public User createUser(User user) {
- usersMap.put(user.getId(), user);
- return usersMap.get(user.getId());
- }
- public User updateUser(User user) {
- if (usersMap.get(user.getId()) != null) {
- usersMap.get(user.getId()).setName(user.getName());
- } else {
- usersMap.put(user.getId(), user);
- }
- return usersMap.get(user.getId());
- }
- public User deleteUser(int id) {
- User userResponse = usersMap.remove(id);
- return userResponse;
- }
- }
package com.kb.rest.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.kb.rest.model.User;
//Just to avoid DB calls in this example, Assume below data is interacting with DB
@Repository
public class UserDAO {
static HashMap<Integer, User> usersMap = new HashMap<Integer, User>();
public UserDAO() {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setAge(20);
user1.setName("raj");
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(2);
user2.setAge(21);
user2.setName("ram");
usersMap.put(1, user1);
usersMap.put(2, user2);
}
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>(usersMap.values());
return userList;
}
public User getUserForId(int id) {
User user = usersMap.get(id);
return user;
}
public User createUser(User user) {
usersMap.put(user.getId(), user);
return usersMap.get(user.getId());
}
public User updateUser(User user) {
if (usersMap.get(user.getId()) != null) {
usersMap.get(user.getId()).setName(user.getName());
} else {
usersMap.put(user.getId(), user);
}
return usersMap.get(user.getId());
}
public User deleteUser(int id) {
User userResponse = usersMap.remove(id);
return userResponse;
}
}We have created DAO class to support all the CRUD operations
We have used a usersMap to store user details(just to avoid DB interaction)
In the constructor , we have added 2 user details in the userMap.
and all the other methods will use this userMap to read,insert,update and delete the user details.
Step 7
Build and deploy the project
Step 8
Let’s see the output of all CRUD operations by using Advanced Rest client
POST
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/create
Select content type “application/json”
Request body
- {
- "age": 30,
- "id": 3,
- "name": "John"
- }
{
"age": 30,
"id": 3,
"name": "John"
}Select POST method
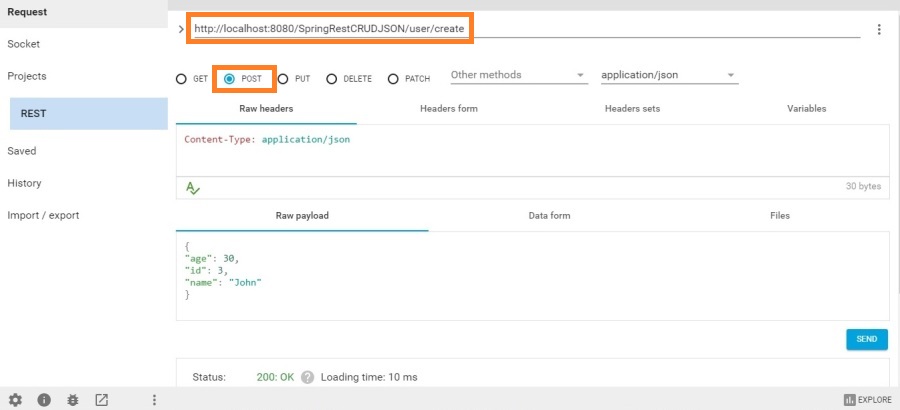
We can see 200 status in the response.
GET
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/getAllUsers
Select GET method
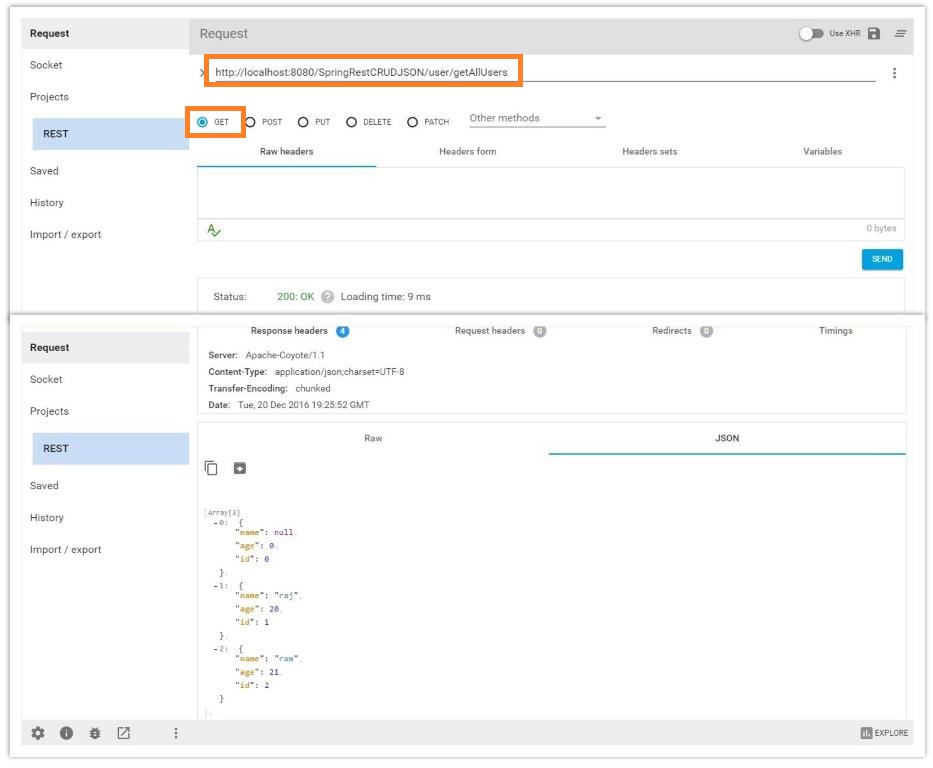
GET with specific user ID
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/getSpecificUser/1
Select GET method
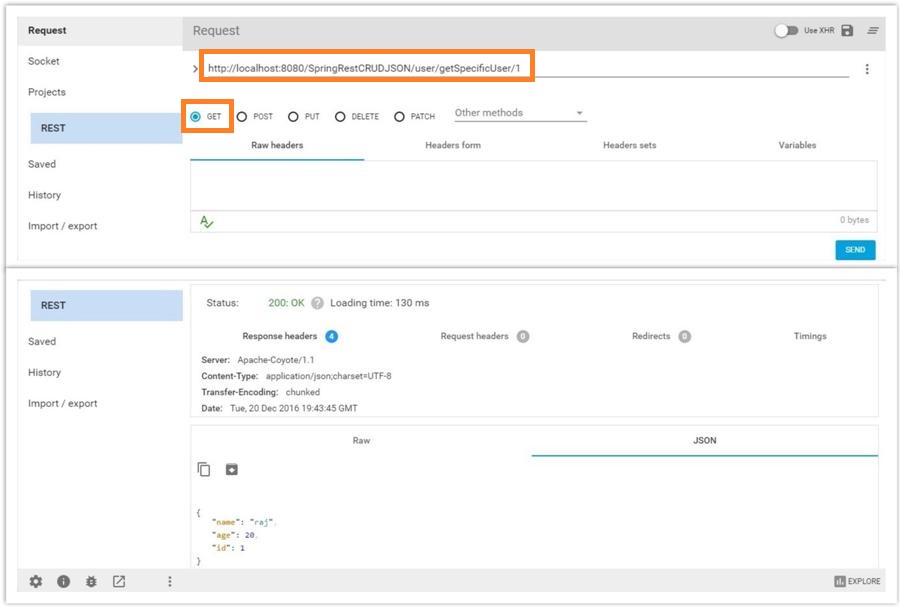
PUT
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/updateUser
Select content type “application/json”
Request body
- {
- "age": 30,
- "id": "3",
- "name": "John"
- }
{
"age": 30,
"id": "3",
"name": "John"
}Select PUT method
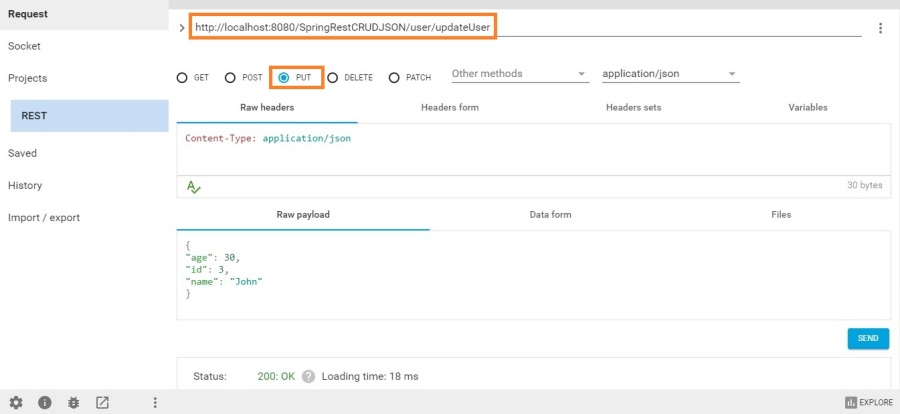
We can see 200 status in the response.
DELETE
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/deleteUser/3
Select DELETE method
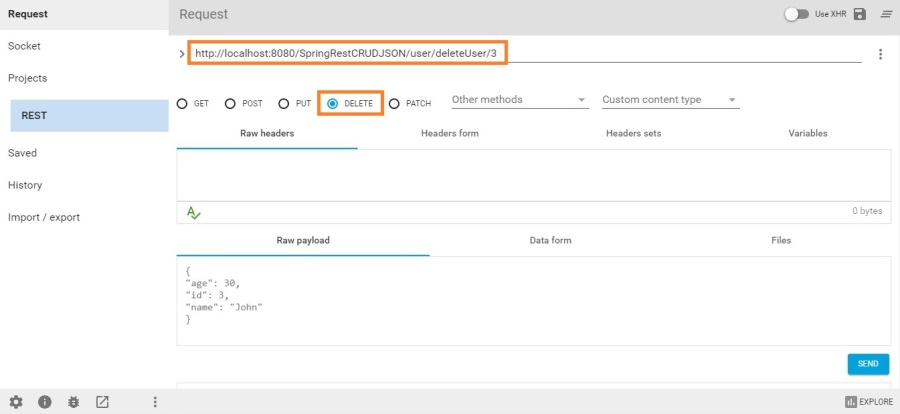
Now try to fetch this record using GET to verify whether it’s deleted or not
http://localhost:8080/SpringRestCRUDJSON/user/getSpecificUser/3
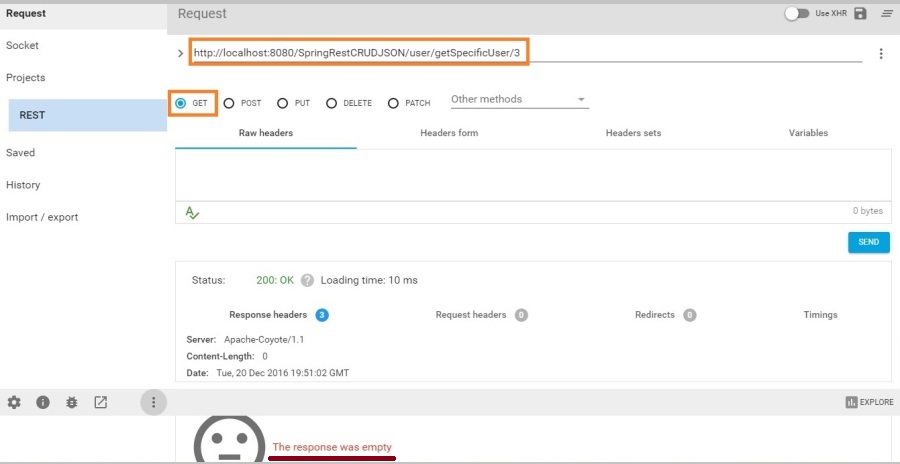
We can see the record got deleted.

Can you please tell me why you have loaded spring-mvc.xml file twice once in init-param and another time in context-param? Is it ok to load it just once either in init-param or within context-param tag?
Thanks
Thanks !!!
you Explain each part.